A stock split is a corporate action that increases the number of a company’s outstanding shares, effectively lowering the price of each share. While the idea of owning more shares for the same total investment might sound appealing, understanding how stock splits work and their impact on your investments is crucial for any investor.
In this blog, we will explore what stock splits are, how they work, the reasons behind them, and how they can impact both the stock price and your portfolio.
What is a Stock Split?
A stock split occurs when a company issues additional shares to its existing shareholders. The split increases the total number of shares in circulation, while the value of each share is reduced proportionally. For example, in a 2-for-1 stock split, an investor would receive two shares for every one they previously owned, but the price of each share would be halved.
The main benefits of stock splits include improved affordability for retail investors and higher market participation. It’s important to note that while the number of shares you own increases after a stock split, the total value of your investment does not change.
For instance, if you held 100 shares worth $100 each before a 2-for-1 split, you would own 200 shares worth $50 each after the split. The total value of your holdings would remain the same at $10,000.
Reasons Companies Implement Stock Splits
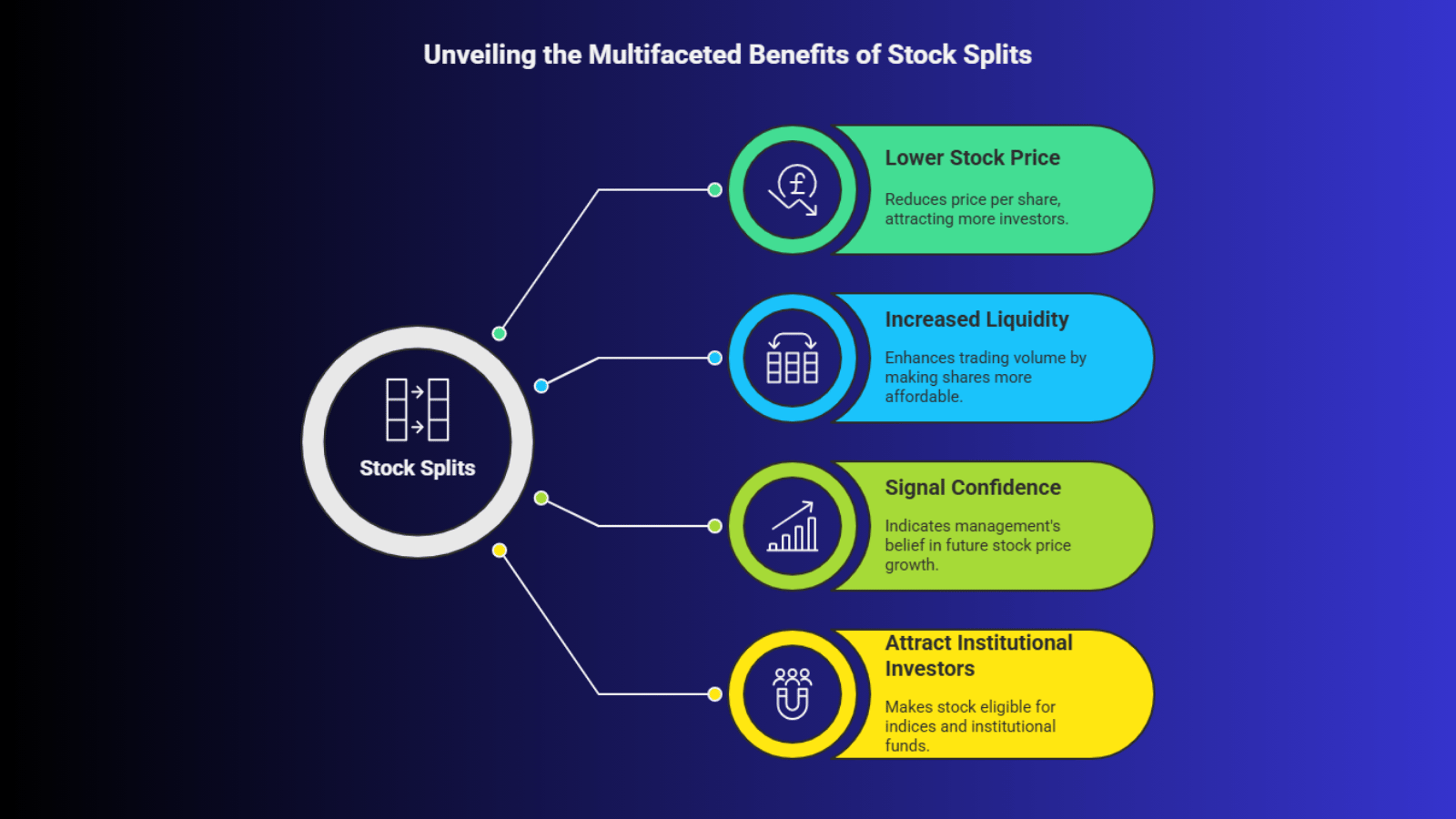 Companies typically announce stock splits for several reasons, including:
Companies typically announce stock splits for several reasons, including:
1. To Make Shares More Affordable
One of the most common reasons for a stock split is to lower the price of the stock, making it more accessible to a broader range of investors. When a stock price becomes very high, it can become less appealing to retail investors. By splitting the stock, the company reduces the price per share, making it easier for more people to buy shares.
For example, if a stock is trading at $1,000 per share, many investors may find it out of their budget. A stock split brings the price down, allowing more people to invest in the company without the need to change the total market capitalization.
2. To Increase Liquidity
Stock splits can increase the liquidity of a stock by making it more affordable and accessible to a larger pool of investors. With more shares available at a lower price, the stock becomes easier to trade, which can lead to higher trading volume.
3. To Signal Confidence in Future Growth
Companies may also use stock splits to signal that they are confident in their future growth. A stock split often happens after a company has experienced significant growth in stock price, suggesting that management believes the price will continue to rise. Investors may view this as a sign of confidence in the company’s prospects.
4. To Attract Institutional Investors
For companies that are trying to attract institutional investors or index funds, stock splits may make sense. Many institutional investors, such as mutual funds, prefer investing in stocks that are priced within a certain range. A lower stock price after a split may make the stock more eligible for inclusion in various indices or appeal to institutional funds.
Investors often evaluate the benefits of stock splits as a signal of company confidence and long-term growth strength.
How Stock Splits Affect Your Investment
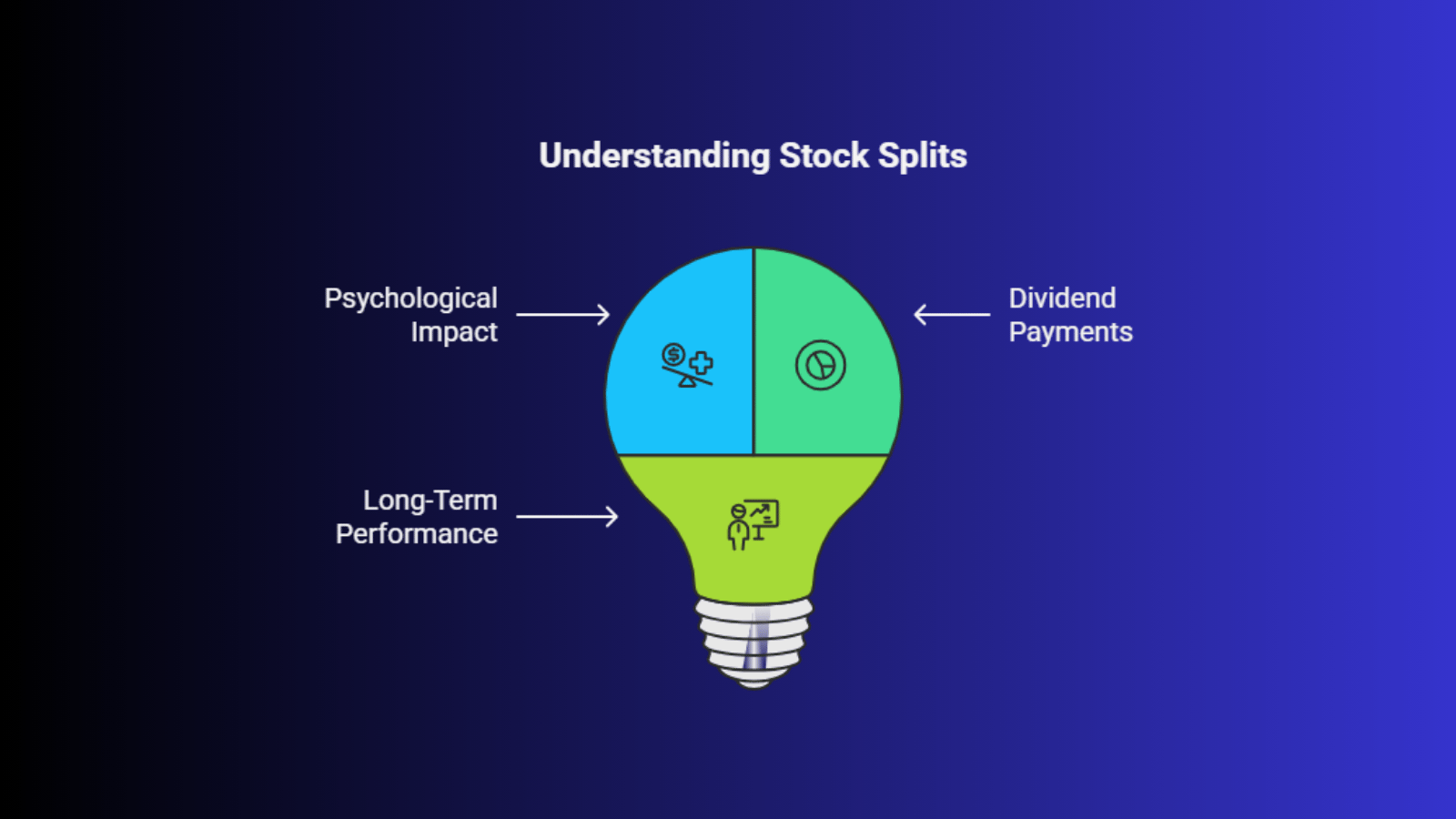 While stock splits do not affect the total value of your investment directly, they can still impact you as an investor in several ways:
While stock splits do not affect the total value of your investment directly, they can still impact you as an investor in several ways:
1. Psychological Impact
The most immediate effect of a stock split is the psychological impact it has on investors. Seeing a lower share price after a split can create the illusion of a bargain, even though the value of the stock has not changed. This could encourage more buying activity, leading to potential short-term price increases.
However, it's important to remember that a stock split does not add value to the company. The company’s fundamentals and future performance will continue to drive the stock price, not the split itself.
2. Impact on Dividend Payments
For companies that pay dividends, stock splits can also impact the dividend payout. After a stock split, the dividend payment is typically adjusted to reflect the increased number of shares. While the dividend per share may decrease, the total dividend payout for investors should remain proportional to the number of shares they hold.
For example, if a company pays $1 in dividends per share before the split, and you held 100 shares, you would receive $100 in dividends. After a 2-for-1 split, you would own 200 shares, but the dividend per share might decrease to $0.50. As a result, you would still receive $100 in total dividends.
3. Long-Term Performance
Stock splits are generally seen as a positive signal, but they don’t directly affect the long-term performance of the company. A stock split doesn’t change the company’s market capitalization or future growth prospects. However, it may lead to increased investor interest, which could drive up demand and potentially increase the stock price in the short term.
In the long run, the value of your investment will still depend on the company's performance, earnings growth, and overall market conditions.
Types of Stock Splits
While the most common stock split is the 2-for-1 split, companies can implement other variations, including:
Type of Stock Split | How It Works | Example Impact on Shares & Price | Purpose |
2-for-1 Split | Each existing share is split into two new shares | 1 share at ₹1,000 becomes 2 shares at ₹500 | Improves affordability and liquidity |
3-for-1 Split | Each share is split into three new shares | 1 share at ₹900 becomes 3 shares at ₹300 | Expands retail investor participation |
4-for-1 Split | Each share is split into four new shares | 1 share at ₹2,000 becomes 4 shares at ₹500 | Increases trading activity |
5-for-1 Split | Each share is split into five new shares | 1 share at ₹1,250 becomes 5 shares at ₹250 | Makes high-priced stocks accessible |
Reverse Stock Split (1-for-2, 1-for-5, etc.) | Multiple shares are merged into one | 2 shares at ₹200 become 1 share at ₹400 | Avoids delisting and improves price perception |
Bottom Line
Stock splits are a corporate strategy that companies use to make their shares more accessible, increase liquidity, and signal confidence in their growth potential. While a stock split does not change the total value of your investment, it can create opportunities for investors to buy stocks at lower prices and may generate greater trading volume and investor interest.
Understanding the benefits of stock splits can help traders target high-liquidity opportunities after a split announcement. As an investor, it’s important to focus on the company’s fundamentals and long-term growth potential rather than being swayed by the temporary effects of a stock split. By understanding how stock splits work and evaluating the company’s financial health, you can make more informed decisions about your investments.
Log in today to explore stocks with upcoming splits and understand how these events may affect your portfolio.
