Investing without a clear diversification strategy exposes your money to avoidable risks. Financial markets move in cycles. Different asset classes, sectors, and regions perform differently across time periods. When investors concentrate their money in a single asset or theme, they become vulnerable to market volatility and sudden downturns. This is why building a diversified portfolio is one of the most important principles of long-term investing.
A diversified portfolio helps smooth returns, reduce risk, and create stability across market conditions. Mutual funds make this process simpler and more accessible for investors of all experience levels. Through mutual fund diversification, investors can spread their money across multiple securities, sectors, and asset classes without having to manage each investment individually.
This guide explains what diversification truly means, why mutual funds are ideal for diversification, and how you can structure a diversified portfolio using different types of mutual funds to achieve long-term financial goals.
What Portfolio Diversification Really Means
Portfolio diversification refers to the practice of spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and instruments to reduce overall risk. Instead of relying on a single stock, sector, or market trend, investors distribute their capital in a way that minimizes the impact of poor performance in any one area.
A well-structured diversified portfolio includes a mix of equities, debt instruments, and sometimes alternative assets. When one asset class underperforms, another may provide stability or positive returns, helping balance the portfolio’s overall performance.
Mutual fund diversification works on the same principle. Each mutual fund typically invests in a basket of securities rather than a single company. By holding multiple mutual funds with different objectives, investors can achieve diversification across:
Asset classes (equity, debt, hybrid)
Market capitalization (large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap)
Sectors and industries
Investment styles (growth, value, income)
This layered diversification reduces dependency on any single factor and improves long-term resilience.
Why Diversification Matters in Long-Term Investing
Market volatility is inevitable. Economic cycles, interest rate changes, global events, and policy decisions can influence asset prices unpredictably. A diversified portfolio helps investors navigate these uncertainties more effectively.
 Key benefits of diversification include:
Key benefits of diversification include:
Risk reduction: Losses in one investment can be offset by gains or stability in others
Smoother returns: Reduced volatility over long investment horizons
Emotional discipline: Less temptation to panic during market downturns
Consistency: Better ability to stay invested through market cycles
Without diversification, portfolios are more exposed to sharp drawdowns. Mutual fund diversification helps investors avoid this risk while maintaining growth potential.
Why Mutual Funds Are Ideal for Diversification
Mutual funds are one of the most efficient tools for building a diversified portfolio. They offer instant exposure to multiple securities and professional management, making diversification accessible even for investors starting with small amounts.
1. Broad Market Exposure
A single equity mutual fund may invest in 30 to 100 stocks across multiple sectors. This automatically reduces company-specific risk. Instead of relying on the performance of one company, investors benefit from the collective performance of many.
Through mutual fund diversification, investors gain access to industries such as banking, technology, healthcare, consumer goods, and infrastructure without selecting individual stocks.
2. Asset Allocation Flexibility
Mutual funds allow investors to mix and match different fund categories to create a customized diversified portfolio. Equity funds drive long-term growth, debt funds add stability, and hybrid funds balance both.
This flexibility allows portfolios to evolve as goals and risk tolerance change.
3. Accessibility and Affordability
Mutual funds allow investors to start with relatively small investments. SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans) enable regular investing with minimal capital, making diversification achievable even for first-time investors.
This low entry barrier is one of the biggest advantages of mutual fund diversification compared to direct investing.
Key Mutual Fund Categories for a Diversified Portfolio
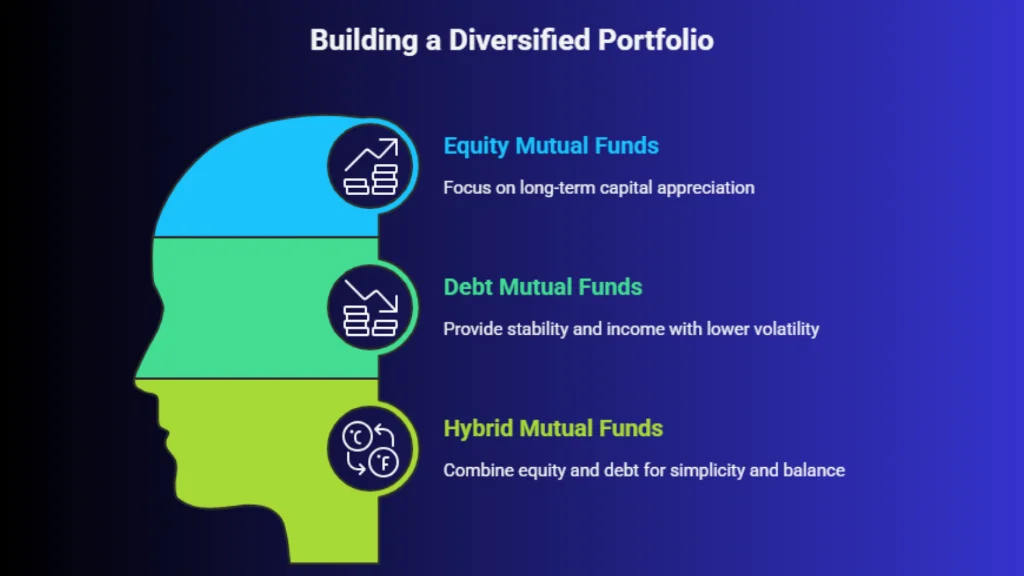 To build an effective diversified portfolio, investors should understand the major mutual fund categories and the role each plays.
To build an effective diversified portfolio, investors should understand the major mutual fund categories and the role each plays.
1. Equity Mutual Funds
Equity mutual funds invest primarily in stocks and are designed for long-term capital appreciation. They form the growth engine of a diversified portfolio.
Large-cap funds offer stability and steady returns
Mid-cap funds provide higher growth potential with moderate risk
Small-cap funds offer aggressive growth with higher volatility
Including a mix of equity funds enhances mutual fund diversification while balancing risk and return.
2. Debt Mutual Funds
Debt mutual funds invest in bonds, treasury bills, and money market instruments. They provide stability, income, and lower volatility compared to equities.
Debt funds help protect a diversified portfolio during market downturns and are suitable for conservative investors or short- to medium-term goals.
3. Hybrid Mutual Funds
Hybrid funds combine equity and debt in a single portfolio. They automatically rebalance asset allocation, making them ideal for investors seeking simplicity and lower volatility.
Hybrid funds play a crucial role in mutual fund diversification by offering both growth and stability in one product.
How to Structure a Diversified Mutual Fund Portfolio
There is no universal formula for building a diversified portfolio. The right structure depends on individual factors such as age, income stability, financial goals, and risk appetite.
Investor Profile | Investment Horizon | Portfolio Allocation Approach | Objective |
Younger Investors | Long-term | Higher allocation to equity mutual funds to maximize compounding and growth | Build wealth through long-term capital appreciation and enhanced mutual fund diversification across growth assets |
Conservative Investors | Short- to medium-term | Higher exposure to debt and hybrid mutual funds for stability | Preserve capital, reduce volatility, and generate predictable returns while maintaining diversification |
Balanced Investors | Medium- to long-term | Mix of equity, debt, and hybrid mutual funds | Achieve steady growth with controlled risk across market cycles using a diversified portfolio approach |
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Diversification
While diversification is powerful, investors should avoid over-diversification. Holding too many similar funds can dilute returns without reducing risk.
 Effective mutual fund diversification focuses on quality, complementary funds rather than quantity.
Effective mutual fund diversification focuses on quality, complementary funds rather than quantity.
Other mistakes include:
Chasing recent performance
Ignoring asset allocation
Neglecting risk tolerance
Failing to review the portfolio periodically
Long-Term Benefits of a Diversified Portfolio
A well-constructed diversified portfolio helps investors stay invested during market volatility and achieve long-term wealth creation. It shifts the focus from short-term returns to consistent growth and risk management.
Mutual fund diversification allows investors to benefit from professional management, broad market exposure, and disciplined investing without complexity.
Making the Right Investment Choice
Building a diversified portfolio with mutual funds is one of the most effective ways to manage risk and grow wealth over time. By spreading investments across asset classes and fund categories, investors can reduce volatility and stay aligned with long-term financial objectives.
Instead of timing the market or chasing trends, mutual fund diversification encourages consistency, discipline, and informed decision-making.
If you are looking to build or enhance a diversified portfolio, log in to your account today to explore a wide range of mutual fund options. You can start investing through SIPs and gradually strengthen your portfolio in line with your financial goals and risk profile.
