Investing in international mutual funds can significantly enhance your portfolio by providing access to global markets. While domestic markets are familiar, overseas investments offer diversification, helping reduce country-specific risks and boosting growth potential. In this blog, we’ll discuss why global exposure is essential, the types of international funds available, and how to begin with small recurring purchases through SIPs.
What Are International Mutual Funds?
International mutual funds invest in companies outside of India, offering exposure to foreign markets. These funds may focus on specific countries like the United States or Europe, or invest across multiple global regions. Some funds track global indices, while others are actively managed, selecting stocks based on specific sectors such as technology, healthcare, or consumer growth.
Investing internationally allows you to tap into companies that aren’t available in Indian markets, broadening your investment horizons. Returns can also be influenced by currency movements, adding an extra layer of potential growth or risk.
Why Global Exposure Matters?
Global exposure strengthens a portfolio by spreading investments across countries, currencies, and economic cycles. While it offers meaningful diversification and growth opportunities, it also introduces certain risks. When you start with small recurring purchases, market volatility has less impact, and investing becomes more disciplined and manageable over time.
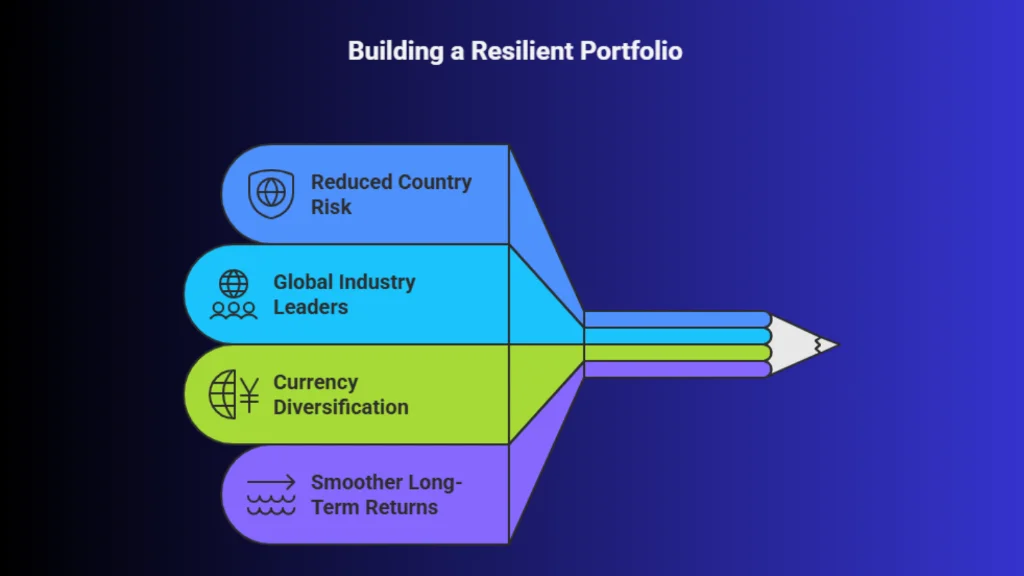 1. Reduced Country Risk
1. Reduced Country Risk
Investing only in one country ties your portfolio’s performance to that nation’s economy, policies, and political environment. Global exposure reduces this dependence by spreading investments across multiple regions. If the Indian market faces a slowdown due to regulatory changes, inflation, or economic stress, global holdings may help balance overall returns.
Pros:
Reduces reliance on a single economy
Protects against local market downturns
Helps stabilize portfolio performance over time
Cons:
Global economic crises can impact multiple markets at once
Political or regulatory risks in foreign countries can affect returns
2. Access to Global Industry Leaders
Many of the world’s most influential companies are listed outside India. Global investing allows participation in sectors and businesses that are not fully represented in domestic markets, such as advanced technology, global consumer brands, and cutting-edge healthcare companies.
Pros:
Exposure to global innovators and market leaders
Participation in high-growth sectors is unavailable locally
Broader sector diversification
Cons:
Limited control over corporate governance standards
Performance may be affected by global competition and regulations
3. Currency Diversification
When you invest internationally, returns are influenced not only by market performance but also by currency movements. A weakening rupee can increase the value of foreign investments when converted back to domestic currency.
Pros:
Acts as a hedge against rupee depreciation
Helps preserve purchasing power over time
Adds an additional layer of diversification
Cons:
Currency volatility can reduce returns
Short-term exchange rate movements can create uncertainty
4. Smoother Long-Term Returns
Different countries and regions perform well at different times. Global exposure reduces volatility by balancing strong and weak market cycles across geographies.
Pros:
Reduces sharp fluctuations in portfolio value
Improves consistency of returns over long periods
Supports better risk management
Cons:
May limit upside during strong domestic market rallies
Requires patience to see long-term benefits
Better Risk-Adjusted Returns
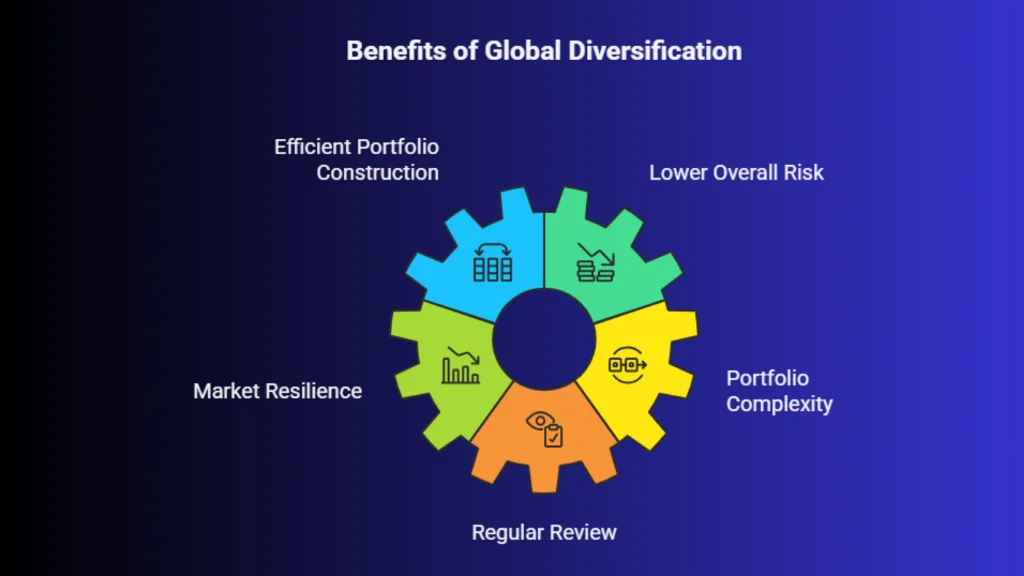 Global diversification improves the balance between risk and return by combining assets that do not move in the same direction at the same time.
Global diversification improves the balance between risk and return by combining assets that do not move in the same direction at the same time.
Pros:
More efficient portfolio construction
Lower overall risk for similar return potential
Better resilience during uncertain markets
Cons:
Slightly higher complexity in portfolio management
Requires regular review and rebalancing
Global exposure is a powerful tool when used thoughtfully, helping investors build stronger, more adaptable portfolios aligned with long-term financial goals.
Types of International Mutual Funds
There are several types of international mutual funds, each catering to different investment needs. You can start with small recurring purchases to build global exposure without putting in a large amount at once.
1. US-Focused Equity Funds
These funds invest primarily in American companies. They are ideal for investors who want exposure to global sectors like technology, healthcare, and consumer brands that dominate international markets.
2. Global Diversified Funds
These funds invest across multiple countries and regions, reducing concentration risk. They provide exposure to both developed and emerging markets, making them suitable for well-rounded global diversification.
3. International Index Funds
These funds track major global indices and offer a low-cost way to gain access to international markets. Ideal for passive investors looking for diversified, global exposure at a fraction of the cost.
4. Emerging Market Funds
Investing in emerging economies provides opportunities for growth in regions with higher growth potential but at a higher risk.
Fund Type | What They Invest In | Example Exposure | Risk Level | Suitable For |
US-Focused Equity Funds | Companies listed in the United States | Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Google, Johnson & Johnson | Moderate | Investors seeking exposure to global technology, healthcare, and consumer leaders |
Global Diversified Funds | Multiple countries across developed and emerging markets | US, Europe, Japan, China, India, Brazil | Moderate | Investors looking for balanced global diversification with reduced country risk |
International Index Funds | Major global indices excluding the home country | MSCI World Index, S&P Global 100 | Low to Moderate | Passive investors who want low-cost, broad international exposure |
Emerging Market Funds | Fast-growing developing economies | China, India, South Korea, Taiwan, Brazil | High | Investors with higher risk tolerance seeking long-term growth opportunities |
How to Choose the Right International Fund
Choosing the right international fund is an important step toward building a well-diversified portfolio. Since global markets behave differently from domestic ones, it is essential to evaluate international funds carefully rather than selecting them based only on recent performance. A thoughtful approach helps reduce risk and improves the chances of steady long-term returns.
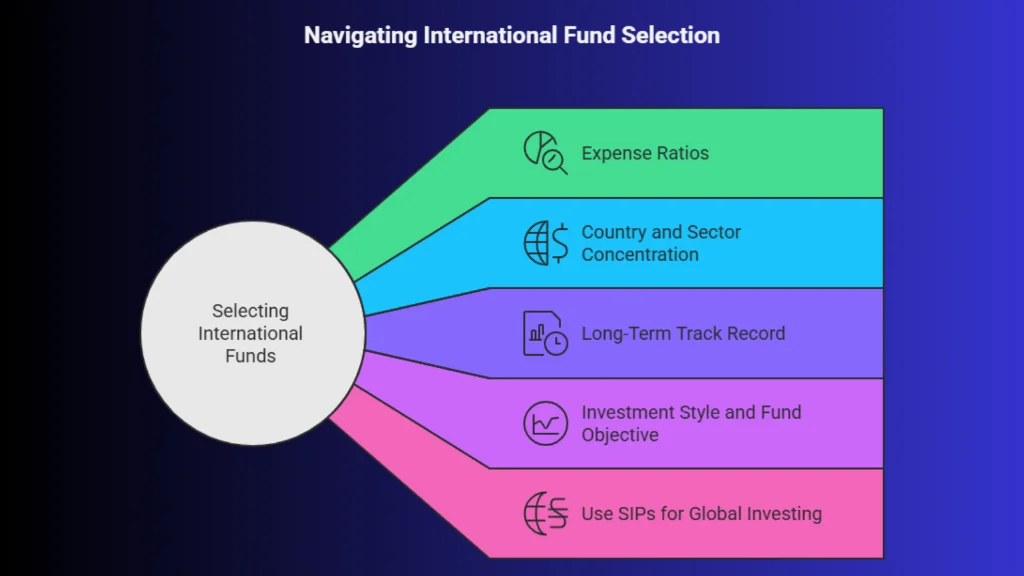 1. Expense Ratios: Expense ratios play a major role in determining how much of your return you actually keep. International funds often involve additional costs related to foreign investing, which makes it even more important to choose funds with lower expense ratios.
1. Expense Ratios: Expense ratios play a major role in determining how much of your return you actually keep. International funds often involve additional costs related to foreign investing, which makes it even more important to choose funds with lower expense ratios.
Over long periods, even small differences in fees can significantly reduce overall returns. Comparing costs across similar funds and favoring low-cost options can help maximize compounding over time.
2. Country and Sector Concentration: Not all international funds are truly diversified. Some may be heavily focused on a single country, such as the United States, or concentrated in a few sectors like technology or healthcare.
While concentration can boost returns during strong market cycles, it also increases risk. Review the fund’s country allocation and sector exposure to ensure it aligns with your risk tolerance. A balanced mix across regions and industries helps reduce the impact of downturns in any one area.
3. Long-Term Track Record: While short-term performance can be tempting, it often reflects temporary market trends. A fund’s long-term track record provides better insight into how it performs across different market cycles.
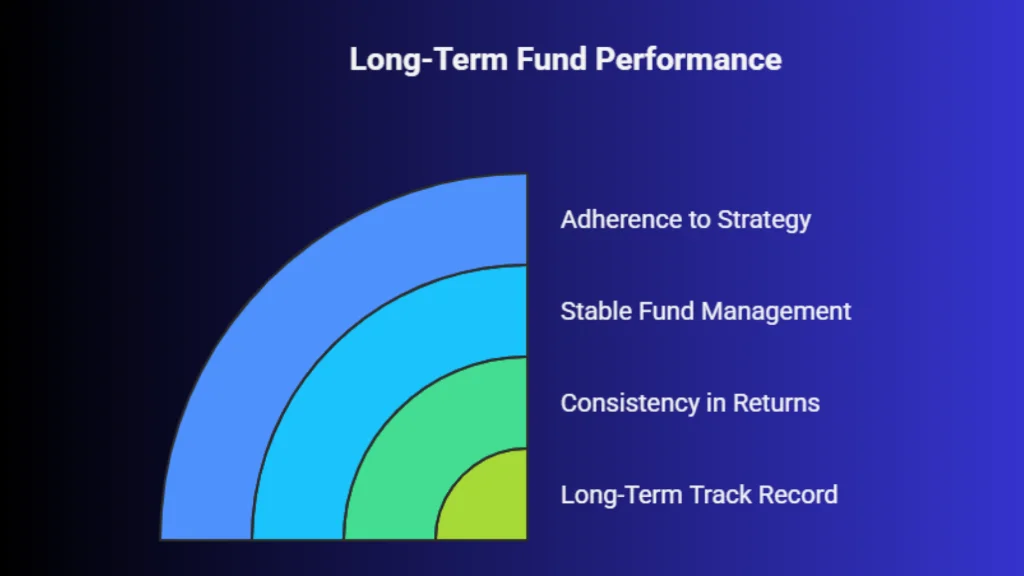 Look for consistency in returns, stable fund management, and adherence to the stated investment strategy. Funds that have delivered reasonable performance over time are often more reliable than those driven by short-term spikes.
Look for consistency in returns, stable fund management, and adherence to the stated investment strategy. Funds that have delivered reasonable performance over time are often more reliable than those driven by short-term spikes.
4. Investment Style and Fund Objective: Understand whether the fund follows an active or passive approach and how it fits into your overall portfolio.
Index-based international funds offer broad exposure and lower costs, while actively managed funds aim to outperform benchmarks but may involve higher risk and fees.
5. Use SIPs for Global Investing: Starting a Systematic Investment Plan in international funds can reduce the impact of market volatility.
Regular investments help average out costs and encourage disciplined investing, making global exposure easier to manage over the long term.
Selecting the right international fund is about balance, consistency, and alignment with your long-term financial goals.
Making the Investment Decision
International mutual funds are best suited for long-term growth, providing a balanced portfolio with exposure to both domestic and global markets. By combining international funds with domestic equity funds, you create a more resilient portfolio that can withstand different economic conditions.
If you’re ready to explore global exposure, log in to your account and start with small recurring purchases or begin an SIP to gradually build an international portfolio with confidence.
