Traditional banking has served as the backbone of the global financial system for decades. From deposits and payments to lending and settlements, banks have enabled economic growth at scale. However, most banking infrastructure was designed long before today’s digital expectations. As transaction volumes rise and customers demand faster, cheaper, and more transparent services, the limitations of legacy systems are becoming increasingly visible.
This is where blockchain banking enters the conversation. Rather than dismantling existing banks, blockchain technology offers a way to modernize how financial data is recorded, verified, and shared. The evolution of blockchain in traditional banking is not about disruption alone. It is about rebuilding trust, efficiency, and resilience in financial systems that must operate at a global scale.
Understanding Blockchain in Simple Terms
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions securely and transparently. Once information is added to the ledger, it cannot be changed without agreement from the network. This makes blockchain records tamper-resistant and highly reliable.
Unlike traditional databases controlled by a single institution, blockchain operates across multiple participants. Each participant maintains a synchronized copy of the ledger. This structure eliminates the need for constant reconciliation between parties, which is one of the biggest sources of delay and cost in banking operations.
In blockchain banking, this shared ledger becomes the foundation for payments, settlements, and record keeping. When applied thoughtfully, blockchain in traditional banking can reduce friction without compromising regulatory oversight or customer protection.
Why Traditional Banking Needs Structural Change
Despite digital interfaces and mobile apps, many banking processes still rely on outdated back-end systems. These systems struggle to keep up with modern transaction volumes and cross-border complexity.
Key challenges include:
Settlement delays that take days instead of minutes
High costs for international transfers
Data silos across departments and institutions
Manual reconciliation is prone to errors
Rising fraud and compliance risks
Blockchain banking directly addresses these inefficiencies by providing a unified, verifiable source of truth. This is why blockchain in traditional banking is increasingly viewed as an infrastructure upgrade rather than a speculative technology.
Key Ways Blockchain Can Transform Banking Operations
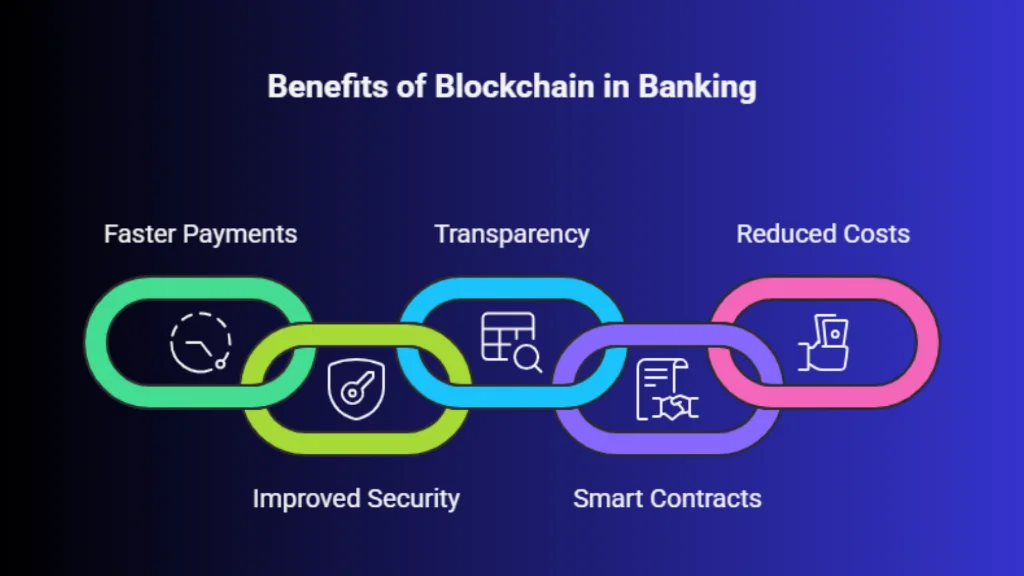 Blockchain is reshaping how banks handle payments, security, and operational efficiency by introducing shared, tamper-resistant digital ledgers. These changes address long-standing inefficiencies in traditional banking systems while improving speed, transparency, and trust across financial operations.
Blockchain is reshaping how banks handle payments, security, and operational efficiency by introducing shared, tamper-resistant digital ledgers. These changes address long-standing inefficiencies in traditional banking systems while improving speed, transparency, and trust across financial operations.
1. Faster and Cheaper Payments
Cross-border payments often pass through multiple intermediaries, increasing costs and delays. Blockchain enables near real-time settlement by recording transactions directly on a shared ledger.
In blockchain banking, payments can settle within minutes instead of days. This significantly lowers operational costs and improves liquidity management. As blockchain in traditional banking expands, international remittances and corporate payments stand to benefit the most.
For investors, these improvements create new opportunities to start digital banking investments aligned with next-generation payment infrastructure.
2. Improved Security and Fraud Prevention
Each transaction on a blockchain is cryptographically secured and linked to previous records. Altering one transaction would require changing the entire chain, which is practically impossible on a well-designed network.
Blockchain banking enhances security by reducing single points of failure. Banks adopting blockchain in traditional banking frameworks can strengthen fraud detection, improve audit trails, and reduce data manipulation risks.
This increased security is one of the strongest reasons institutions and investors are choosing to start digital banking investments focused on blockchain-enabled platforms.
3. Transparent and Auditable Records
Blockchain creates a single, shared transaction history visible to all authorized participants. This transparency simplifies audits and compliance reporting.
In blockchain banking, regulators can access accurate records in real time rather than relying on delayed reports. This makes blockchain in traditional banking especially attractive for regulatory compliance, trade finance, and interbank settlements.
Transparency builds trust not just between banks, but also with customers and regulators. This trust factor is driving many to start digital banking investments in regulated blockchain solutions.
4. Smart Contracts and Process Automation
Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on a blockchain. They automatically trigger actions when predefined conditions are met.
 In blockchain banking, smart contracts can automate loan disbursements, interest calculations, collateral management, and trade settlements. By embedding logic directly into transactions, blockchain in traditional banking reduces manual intervention and operational delays.
In blockchain banking, smart contracts can automate loan disbursements, interest calculations, collateral management, and trade settlements. By embedding logic directly into transactions, blockchain in traditional banking reduces manual intervention and operational delays.
This automation lowers costs and improves accuracy, making it easier for financial institutions to scale. Investors tracking automation trends often start digital banking investments in firms building smart contract infrastructure.
5. Reduced Operational and Back Office Costs
A significant portion of banking expenses comes from reconciliation, compliance checks, and manual processing. Blockchain minimizes these costs by creating a unified ledger shared across systems.
Blockchain banking eliminates duplicate data entry and reduces human error. Over time, blockchain in traditional banking can significantly lower back office costs, allowing banks to offer better pricing and improved customer experiences.
These cost efficiencies strengthen the business case for institutions and encourage individuals to start digital banking investments tied to operational innovation.
Real World Use Cases of Blockchain in Banking
Banks around the world are already experimenting with blockchain applications. Some focus areas include:
Interbank settlements
Trade finance documentation
Cross-border payments
Digital identity verification
Tokenized assets and securities
These use cases demonstrate that blockchain banking is already moving beyond theory. The gradual adoption of blockchain in traditional banking shows how innovation can coexist with regulatory compliance.
Challenges That Still Need to Be Solved
Despite its potential, blockchain adoption is not immediate or effortless. Several challenges remain.
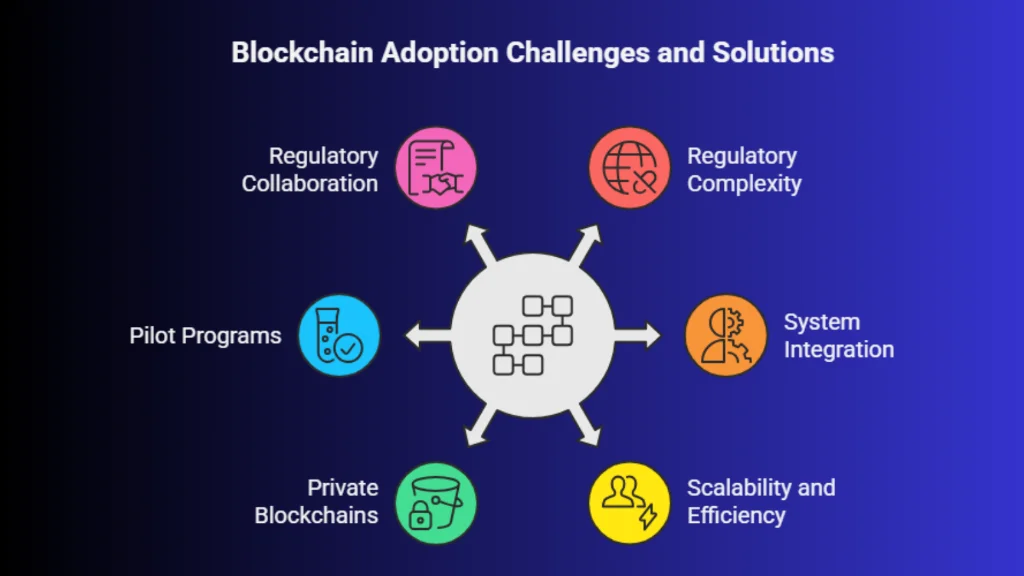 Regulatory frameworks vary across regions, making cross-border implementation complex. Legacy banking systems must integrate with blockchain platforms without disrupting operations. Scalability and energy efficiency are also concerns for certain blockchain networks.
Regulatory frameworks vary across regions, making cross-border implementation complex. Legacy banking systems must integrate with blockchain platforms without disrupting operations. Scalability and energy efficiency are also concerns for certain blockchain networks.
Banks are addressing these issues through private and permissioned blockchains, pilot programs, and collaboration with regulators. These measured approaches ensure blockchain banking evolves responsibly within existing financial systems.
As these challenges are resolved, more participants will confidently start digital banking investments linked to institutional blockchain adoption.
The Future of Blockchain in Traditional Banking
Blockchain is unlikely to replace banks entirely. Instead, the future lies in hybrid models where banks retain customer relationships and compliance roles while leveraging blockchain for infrastructure.
In this future, blockchain in traditional banking supports settlement, identity verification, compliance reporting, and data sharing. Blockchain banking becomes an invisible layer powering faster and more secure services.
This evolution mirrors how cloud computing transformed banking operations without eliminating banks themselves.
What This Means for Investors and Professionals
Understanding blockchain banking is no longer optional for those involved in finance, fintech, or investment strategy. The integration of blockchain in traditional banking signals long-term structural change in financial infrastructure.
For professionals, this creates career opportunities in payments, compliance technology, and digital finance. For investors, it opens pathways to start digital banking investments aligned with long-term technological adoption rather than short-term speculation.
By focusing on regulated, institution-driven blockchain use cases, investors can participate in innovation while managing risk.
How to Start Exploring Blockchain-Driven Banking Opportunities
As blockchain adoption grows, individuals can explore opportunities across fintech platforms, digital banking services, and infrastructure providers.
If you want to position yourself early, you can start digital banking investments through platforms that track fintech innovation. Many investors start digital banking investments gradually, focusing on diversified exposure rather than concentrated bets.
Whether you are a professional, investor, or enthusiast, learning about blockchain banking today prepares you for how finance will function tomorrow. Log in to your account to explore emerging opportunities and insights.
